Funding
DHS Releases 2026/27 Blue Book; RCPA Shares Divisional Analysis
RCPA Shares DHS Secretary Arkoosh Budget Presentation Overview
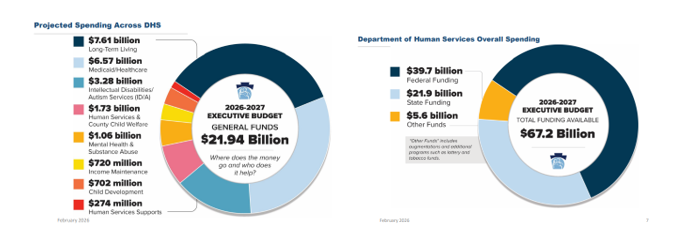
On Friday, February 6, Department of Human Services (DHS) Secretary Val Arkoosh presented an overview of Governor Shapiro’s proposed Fiscal Year (FY) 2026/27 budget and detailed the projected spending across DHS, which totals $21.94 billion in state funding. The Secretary highlighted that all three Medicaid managed care programs, as well as waiver programs for people with intellectual disabilities and autism, are receiving increases, largely driven by patient needs and costs associated with delivering care. The proposed FY 2026/27 budget includes $39.7 billion in federal funding as well as $5.6 billion from augmentations and additional programs, such as lottery and tobacco funds, making the total DHS funding $67.2 billion.
The Secretary expressed how the proposed budget reflects the direct impacts of HR 1, with significant federal funding at risk. The distribution for the 2026/27 budget is based upon the current structure of Medicaid and other federally funded programs, but the Secretary noted that beginning in 2028, changes in Medicaid financing rules will remove $20 billion from Pennsylvania’s Medicaid program over the following decade.
Budget Highlights and Investments
- Investments in Health:
- Food is Medicine: $900,000 (federalizes to $2.3 million) in state funds to launch a pilot program that will provide nutritionally appropriate food to improve quality of life and health outcomes while lowering overall health care costs for Medicaid recipients with significant health care needs.
- Housing Stability: $1 million in state funds (federalizes to $2.5 million) to launch a pilot that will connect people experiencing homelessness to stable housing and services that improve health and care management.
- Reentry Supports: $900,000 in state funds (federalizes to $2.7 million) to provide pre-release coverage (up to 90 days prior to release from a State Correctional Institution) for substance use care and intensive case management.
- Continuing ODP Multi-Year Growth Strategy: Building upon Shapiro’s 2024 multi-year strategy to expand access to home and community-based services and effectively end the emergency waiting list of adults with intellectual disabilities with autism, the proposed budget allots $30 million in state funds, which federalizes to $66.2 million. This will allow for 850 more people to be served in the Community Living Waiver and 400 more people to be served in the Consolidated Waiver.
- Supporting 988 Call Centers and Crisis Services: The proposed budget includes a $10 million investment in the crisis response workforce to help 988 call centers, as well as $5 million in state funds to continue prior year commitments for emergency behavioral walk-in centers.
- Sustaining Early Intervention Rate Increase: The Secretary stated that the EI line item in the executive budget reflects the changing state cost to run the program and not an anticipated cut in funding. The release of the DHS Blue Book will have more information about the total funding with federal match. DHS intends to keep the new, updated rates from the 2025/26 budget, and revised rates will be released soon.
- County Base Mental Health Services Funding: RCPA has confirmed that there will be no allocation increase for county base funding. While previous budgets had included $20 million for county base mental health funding, it was not included in the 2025/26 budget or the proposed 2026/27 budget.
Due to technical difficulties, DHS was unable to record the webinar, but the presentation slides and transcript can both be viewed.
Please contact your RCPA Policy Director with any questions or concerns.
Reminder for Mental Health Safety Net Coalition Meeting on February 13
RCPA will reengage with all members, non-members, and systems-wide behavioral health stakeholders to participate in the Mental Health Safety Net Coalition. The Coalition is focused on developing strategies, activities, and engagement opportunities to support behavioral health funding in the Commonwealth.
The Coalition will have its first meeting on Friday, February 13, 2026, from 12:00 pm – 1:00 pm. This meeting will give the group an opportunity to review last year’s budget, Governor Shapiro’s proposed budget, and initial strategies for the Fiscal Year (FY) 2026/27. It will also give us an opportunity to develop questions for legislators for the DHS budget hearings in late February and early March. Register for the meeting by contacting Emma Sharp, RCPA Policy Associate.
As the group continues to meet, we will develop our overall advocacy blueprint to ensure the communication of our message and stakeholder engagement is focused on protecting and preserving our mental health service delivery system.
The meetings will be held via Microsoft Teams; information will be sent to those interested in the Coalition. RCPA invites all to participate. If you would like to join the Coalition or have any questions, please contact Emma Sharp.
$30M Gift Supercharges Pediatric Care Across PA, From CHOP to Rural ERs, RCPA Member Children’s Hospital Of Philadelphia Featured
Governor Shapiro’s 2026/27 Budget Address Overview
On February 3, 2026, Governor Josh Shapiro delivered his fourth budget address to the Pennsylvania General Assembly. He began the address by commending the significant growth of the Commonwealth over the last three years, highlighting improvements in quality education, agriculture, energy, and becoming the only state in the Northeast with a growing economy.
Shapiro’s 2026/27 proposed budget calls for $53.3 billion in state General Funds expenditures, with Medicaid (32%) and Education (36%) being the largest spend categories. Other expenditures include:
- Human Services and other DHS programs (9%);
- Corrections and Parole (6%);
- Higher Education (4%);
- Debt Service (3%); and
- 10% remaining for all other categories.
The 2026/27 budget also includes supplemental appropriations of $390.3 million to increase the FY 2025/26 General Fund spend to $51.5 billion. The majority of this increase is attributed towards DHS programs and Education through the end of FY 2025/26, with a $374.5 million increase for human services related to increased projections of utilization, caseloads, and enrollments anticipated through June 2026.
Similar to last year’s address, Shapiro called for the legalization and taxation of adult use cannabis as well as taxing and regulating skill games terminals in order to support the proposed 2026/27 expenditure. The budget would also be funded by transferring $4.6 billion from the Budget Stabilization Reserve Fund (Rainy Day Fund) to the General Fund, which would leave the Rainy Day Fund balance at $3.3 billion.
2026/27 Proposed Budget Highlights:
Behavioral Health
- Behavioral Health Medicaid Capitation: The 2026/27 proposed budget includes a 15% increase to $4.4 billion in Medicaid capitation funding to the behavioral and physical HealthChoices programs. This is the amount of money from which behavioral health Medicaid managed care organizations reimburse providers for mental health and SUD treatment services. At this point, how the total capitation funding breaks out between behavioral and physical health is not known. The current fiscal year budget includes $1.95 billion in behavioral health Medicaid capitation.
- Substance Use Disorder Funding: The Department of Drug and Alcohol Programs saw a $300,000 increase in its general operations fund but was otherwise flat-funded. Most of DDAP’s state dollars are passed onto Single County Authorities to fund treatment at the county level.
- Adult Use Recreational Marijuana: The proposed budget included $730 million in anticipated revenue from legalized adult use recreational marijuana, which, if legalized by the legislature, would take effect January 1, 2027.
- Mental Health Services: The proposed budget includes a $65 million (+6.9%) increase, including $10 million to support the 988 network, $7.3 million to expand diversion and discharge programs for individuals with mental illness currently in the criminal justice system, and $5 million to maintain walk-in mental health crisis stabilization centers.
- School Mental Health: Shapiro proposed $100 million for school mental health and safety, totaling in $400 million over his term.
Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
- Intellectual Disabilities Community Waiver: The Governor’s proposed FY 2026/27 budget includes a $76.8 million increase for the Intellectual Disabilities Community Waiver line item, largely intended to maintain existing services and enrollment rather than expand capacity. No funding is currently explicitly proposed for waiting list initiatives.
- ARPA HCBS Funding: One-Time ARPA HCBS funding is ending in 2026. A limited backfill is proposed to continue select initiatives, raising questions about the long-term sustainability of workforce and service enhancements supported with one-time federal funds.
- Minimum Wage Increase: The proposal to increase the minimum wage to $15/hour, effective January 1, 2027, would significantly impact IDD providers without a clearly identified, corresponding waiver rate adjustment in the budget.
- Emphasis on Stability: Overall, the budget proposal shows a focus on maintaining current system stability. Ongoing workforce cost pressures and rate adequacy remain key concerns for IDD service providers.
Community HealthChoices
- The initial release of the Governor’s 2026/27 budget for the Department of Human Services (DHS) includes an increase of 7.47% for Medical Assistance/Community HealthChoices. RCPA will be working with DHS to determine what this increase to the CHC-MCOs will encompass and how this could impact members under the Community HealthChoices program.
While this brief overview provides a snapshot of the Governor’s proposed budget, RCPA Policy Staff will be working with our lobbying partners, healthcare experts, and systems’ stakeholders to provide a thorough analysis of the budget to members. We have confirmed that DHS will be hosting a virtual proposed budget briefing on its portion of the State Budget funding this Friday, February 6, 2026. An invitation was distributed to RCPA members earlier this morning. The virtual briefing will provide some additional details, but the DHS “Blue Book” provides the most detail on certain appropriation lines and should be available in the coming weeks in advance of its hearings with the Senate and House Appropriations Committees.
If you have questions, please contact your respective RCPA Policy Director.
Gov. Shapiro Unveils PA Budget Plan That ‘Builds on Progress’ and Raids the Piggybank
DDAP Awards Nine Grants Totaling $1.2 Million to SCAs for Recovery Housing, Supports for Young Adults
The Pennsylvania Department of Drug and Alcohol Programs (DDAP) is awarding more than $1.2 million to expand access to recovery housing and recovery support services throughout Pennsylvania for young adults 18–24 years old who have opioid or stimulant use disorders. DDAP is awarding grants to nine Single County Authorities (SCA) to fund the effort.
Currently, there are about 430 DDAP-licensed recovery houses across the Commonwealth. The purpose of the Administration’s licensure program is to help empower sustained recovery for individuals with substance use disorder (SUD) by ensuring a network of safe drug and alcohol recovery houses. Drug and alcohol recovery houses are required to be licensed in order to receive referrals from state agencies or state-funded facilities or to receive federal or state funding to deliver recovery house services.
The grant funds will be used to supplement existing resources, ensuring that current services are expanded rather than replaced, and that recovery housing remains accessible and safe through Pennsylvania.
DDAP is awarding nine grants, which will run through September 30, 2026, to the following SCAs serving 14 counties:
- Berks County Council on Chemical Abuse: Berks County
- Blair County Drug and Alcohol Program, Inc.: Blair County
- Columbia Montour Snyder Union Drug & Alcohol Services: Columbia, Montour, Snyder, and Union Counites
- Delaware County Department of Human Services, Division of Drug and Alcohol Programs: Delaware County
- Erie County Office of Drug and Alcohol Abuse: Erie County
- Lackawanna/Susquehanna Office of Drug and Alcohol Programs: Lackawanna and Susquehanna Counties
- Somerset Single County Authority for Drug and Alcohol: Somerset County
- Westmoreland Drug & Alcohol Commission, Inc.: Westmoreland County
- York Adams Drug and Alcohol Commission: York and Adams Counties
Mental Health Safety Net Coalition Meeting Announced for February 13
RCPA will reengage with all members, non-members, and systems-wide behavioral health stakeholders to participate in the Mental Health Safety Net Coalition. The Coalition is focused on developing strategies, activities, and engagement opportunities to support behavioral health funding in the Commonwealth.
The Coalition will have its first meeting on Friday, February 13, 2026, from 12:00 pm – 1:00 pm. This meeting will give the group an opportunity to review last year’s budget, Governor Shapiro’s proposed budget, and initial strategies for the Fiscal Year (FY) 2026/27. It will also give us an opportunity to develop questions for legislators for the DHS budget hearings in late February and early March. Register for the meeting by contacting Emma Sharp, RCPA Policy Associate.
As the group continues to meet, we will develop our overall advocacy blueprint to ensure the communication of our message and stakeholder engagement is focused on protecting and preserving our mental health service delivery system.
The meetings will be held via Microsoft Teams; information will be sent to those interested in the Coalition. RCPA invites all to participate. If you would like to join the Coalition or have any questions, please contact Emma Sharp.

















